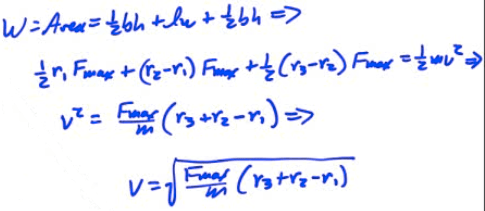What is Work?
Work is the process of moving an object by applying a force
The object must move for work to be done
The force must cause the movement
Work is a scalar quantity
Units are Joules
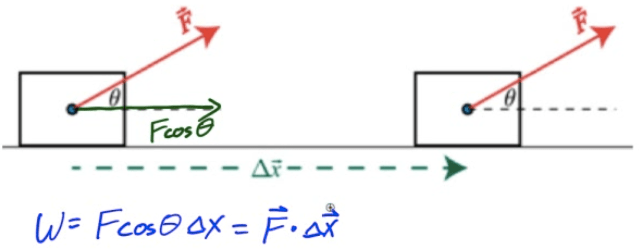
Work in One Dimension
Only the force in the direction of the displacement contributes to the work done
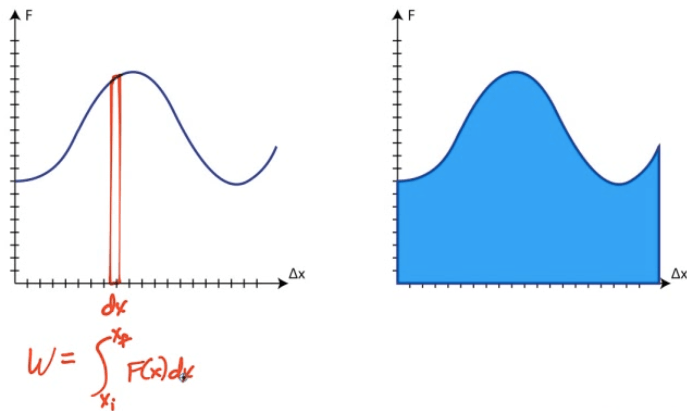
Non-Constant Forces
Work done is the area under the force vs. displacement graph
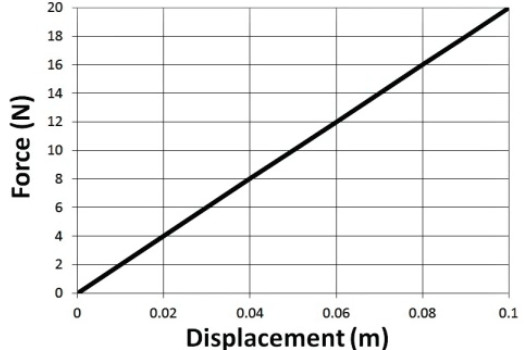
Hooke's Law
The more you stretch or compress a string, the greater the force of the spring
The spring's force is opposite the direction of its displacement from equilibrium
Model this as a linear relationship, where the force applied by the spring is equal to a constant (the spring constant) multiplied by the spring's displacement from its equilibrium (rest) position
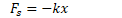
Slope of the graph gives you the spring constant, k (in N/m)
Work Done in Compressing a Spring
A spring obeys Hooke's Law. How much work is done in compressing the spring from equilibrium to some point x?
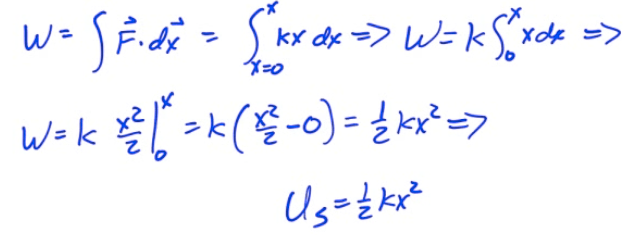
Work Done in Compressing a Non-Linear Spring
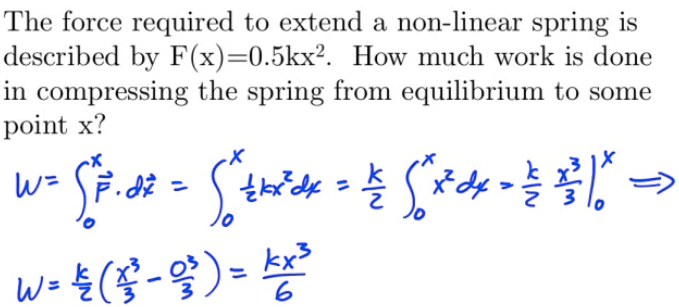
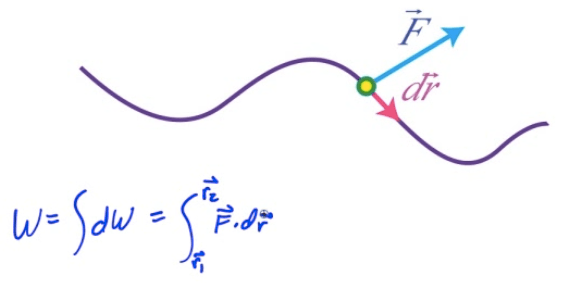
Work in Multiple Dimensions
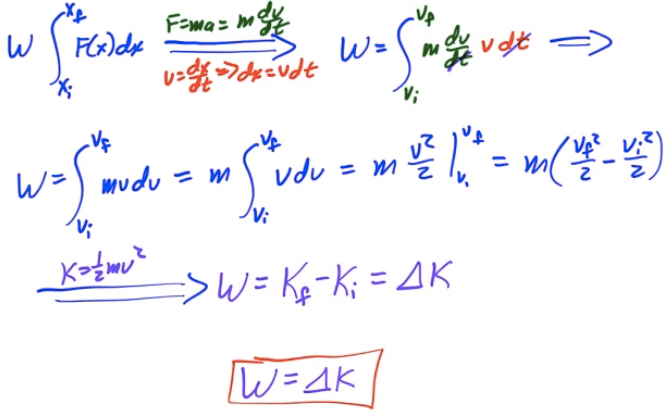
Work-Energy Theorem
Example: Velocity from an F-d Graph
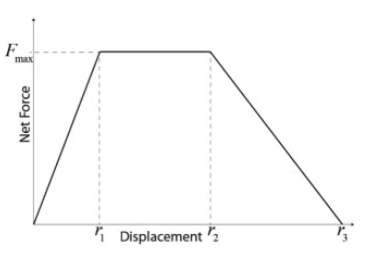
Determine the object's final speed.