Newton's First Law of Motion
An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion, at constant velocity and in a straight line, un line acted upon by a net force
An object will continue in its current state of motion unless an unbalanced force acts upon it
An object at rest will remain at rest unless an unbalanced force acts upon them
Also known as the law of inertia
Force
A force is a push or pull on an object
Unites of force are newtons (N)
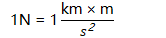
| Contact Force | Field Force |
|---|---|
| Tension Applied Force Friction |
Gravity Electrical Force Magnetic Force |
Net Force
A net force is the vector sum of all the forces acting on an object
If all forces are balanced, there is no net force. This situation is known as translational equilibrium
An unbalanced force is a net force
Equilibrium
Static Equilibrium
Net force on an object is 0
Net torque on an object is 0
Object is at rest
Mechanical Equilibrium
Net force on an object is 0
Net torque on an object is 0
Translational Equilibrium
- Net force on an object is 0
Inertia
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in velocity
Mass actually has two aspects
Inertial mass is how hard it is to change an object's velocity
Gravitational mass is how strongly a gravitational field affects a mass
For the purposes of basic introductory physics, mass and inertia are synonymous
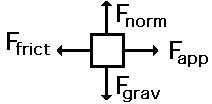
Free Body Diagrams
Tools used to analyze physical situations
Show all the force acting on a single object
Object itself drawn as a dot or rectangle